Customize Universal Collector - PREVIEW
NOTE
The Customize Collectors page is a preview feature in support of our universal collector as part of the data source configuration.
The Custom Universal Collector allows you to define and configure discovery workflows for applications and systems not covered by built-in collectors. This enables organizations to adapt Hydden to unique infrastructure requirements, discover accounts in proprietary or legacy systems, and extend identity governance to the complete application ecosystem.
The customization feature supports various modules with functions to interact (request, receive, and process data) based on different languages, protocols, and URI schemes.
The order of customization is:
- Provide basic information on the Details tab.
- Use the Editor to populate the script with blocks (Types) based on information from the Help module. Preplan what the collector is supposed to achieve, what the requirements are and build the script to match.
- On the Variables tab, set the variables to match your external application's API.
- Use Run Now to run the script, which will create your Schema.
- On the Schema tab, edit the Schema as needed to create mappings. The script created the schema based on the specified API calls to aquire data from the application.
- On the Mappings tab, create your Target and Extended Mappings. Choose the schemas for mapping purposes from the Source Schema and Target Schema drop-downs. Extended mapping data might need to be reviewed on an individual account basis via Global Search. The extended mapping data does not populate in out-of-the-box report.
Editing Custom Collectors
Use the edit button to customize the imported template files. Edit the Details tab first.
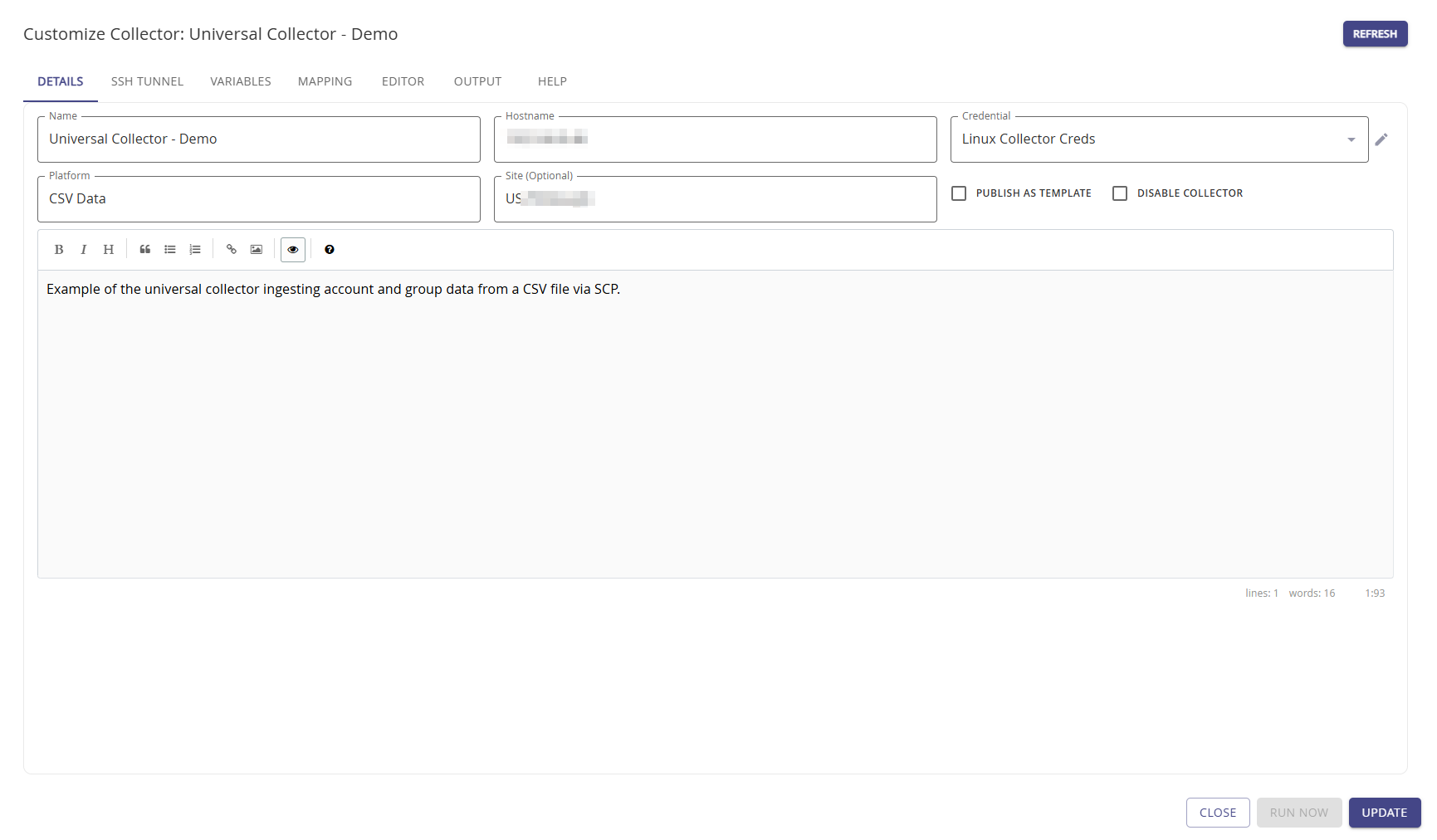
Details Tab
The Details page provides a means to change the basic collector details that were provided when the collector was added for the first time.
- Name
- Hostname
- Credential
- Platform: The platform name should be consistent if you are setting up more than one of the same data collection. The platform name for the Universal Collector can be edited at any time. Options often used are CSV Data, Delimited File, or Application Data.
- Site (Optional)
Once your collector is fully configured, you have the option to Publish as template. Setting the checkbox allows you to easily reuse the base configuration for any new collector.
To disable the collector, set the Disable Collector checkbox.
In the text field add a helpful description what your collector does. In our example we use Example of the universal collector ingesting account and group data from a CSV file via SCP. As such, our platform is CSV Data for this collector.
Click Update to save any changes.
Editor
The Editor tab provides a script file based on the configuration established when the collector was added, a template was selected, and the Universal Collector was customized. The file can also be manually edited. Utilize the Help module to build out the script.
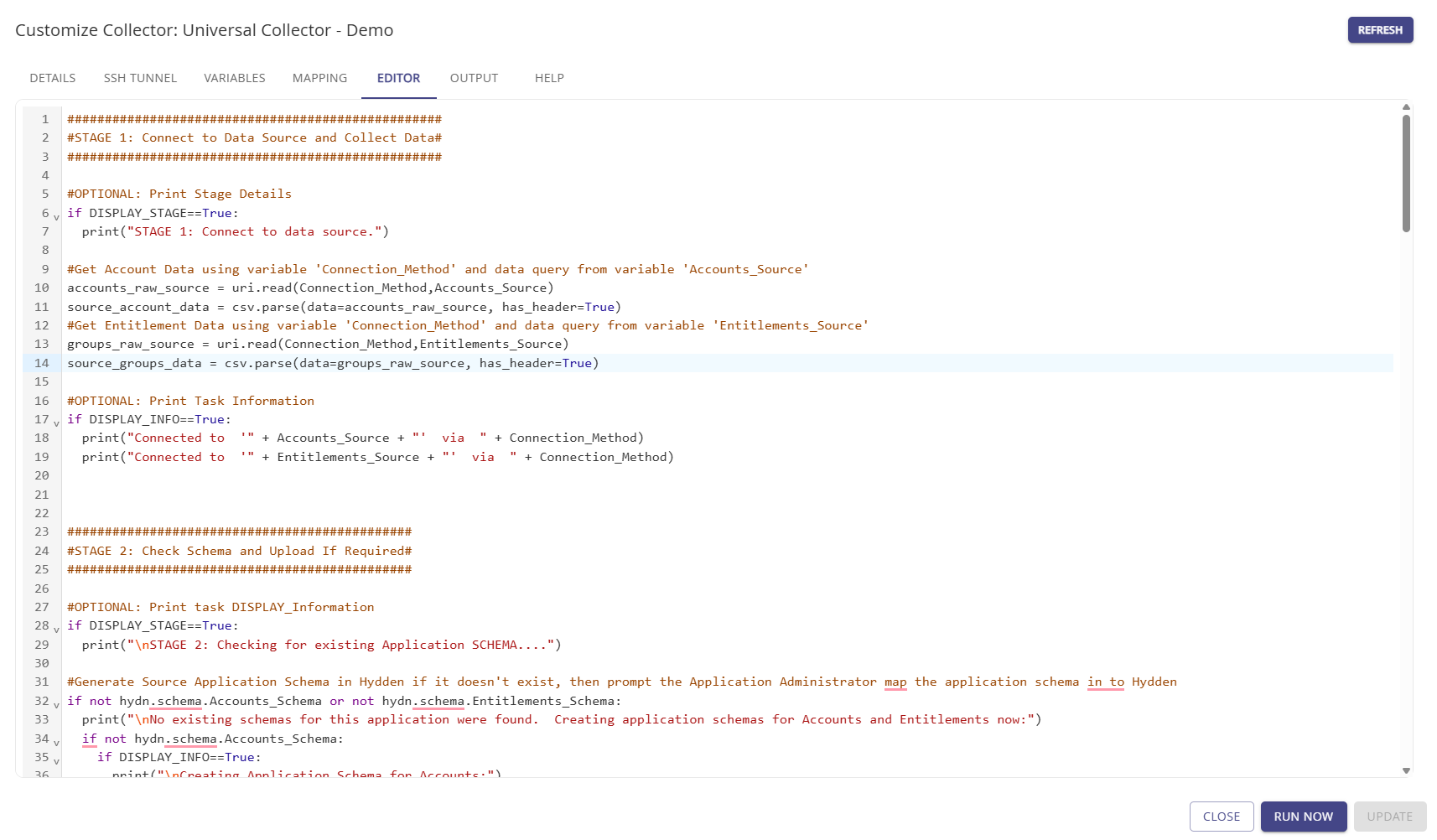
Click Update to save any changes.
Variables
Variables are global in Hydden and any variable added for your collector can be used in reports or for threat rules.
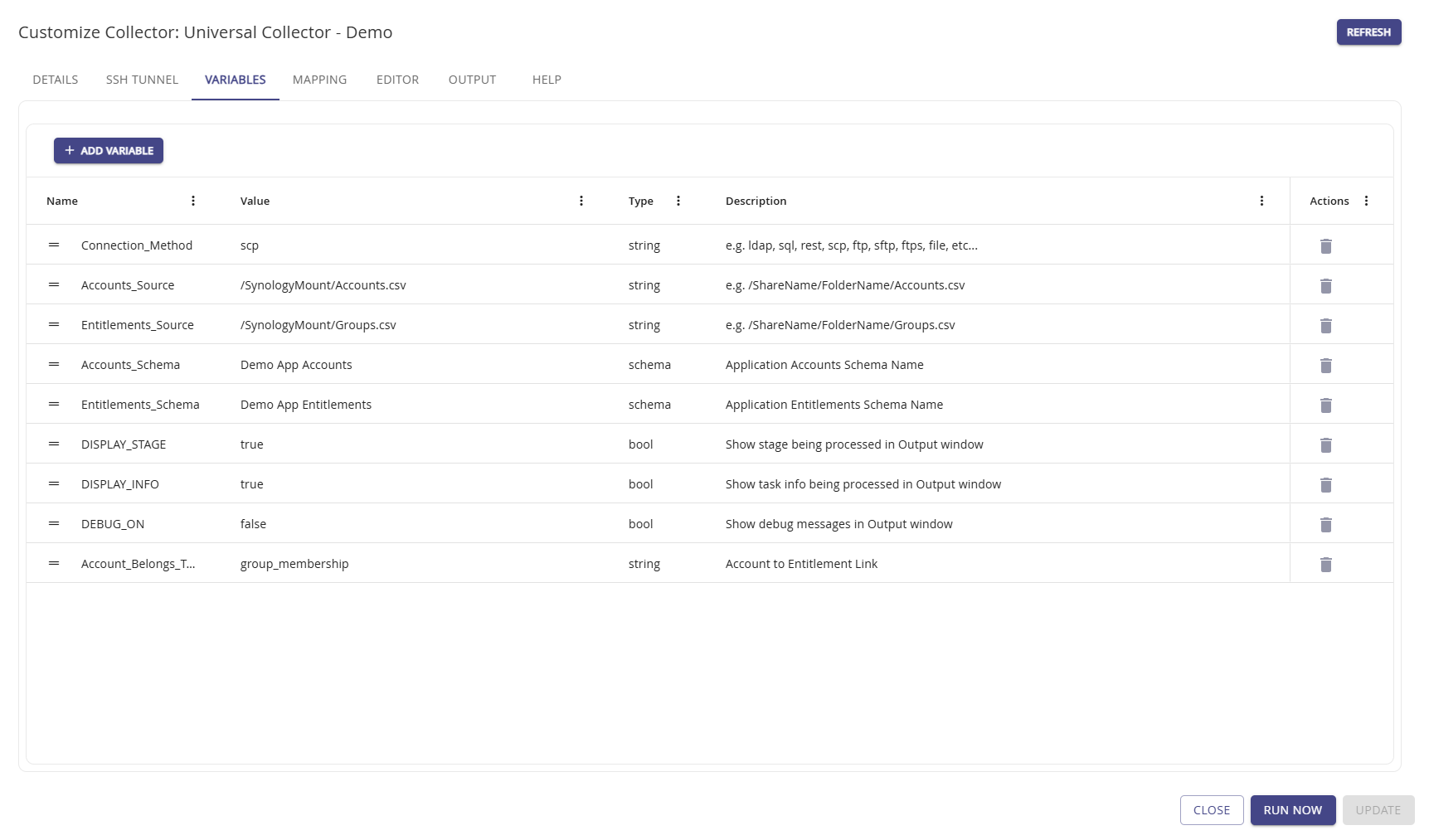
Use Add Variable to add new variables for you specific application needs. Click Update to save any changes.
Usually after adding your variables, your script is ready to run. Click the Run Now button to verify your schema and start the Source to Target Mapping process.
More details to follow on this feature as the preview progresses towards a general available feature.
Schemas
The Schemas tab lists the associated schema details for this collector and the target application. The schema entries are created based on specifications on the variables tab and are created during the script building process. The schema can me
Mapping
Use the Mapping tab to establish data mappings for your data between the source and the target schema. This is the foundation for identity data collection from various sources, which allows the analysis and comparison no matter what is collected from where. It's the key to compare apple to oranges and provide a insights on the identity posture of an organization across all systems.
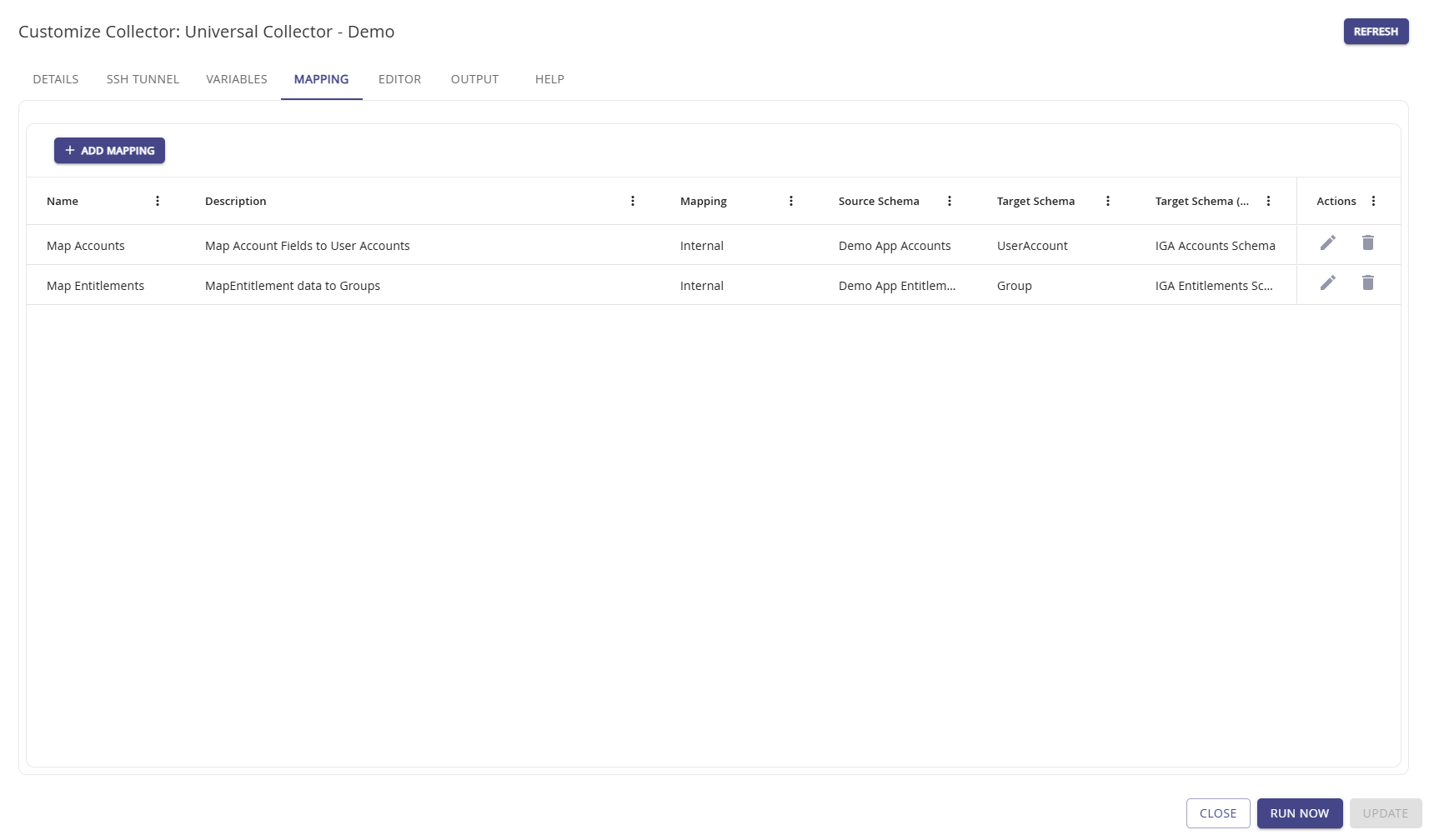
Use Add Mapping to create new data associations between your source data and Hydden's target data. The table grid fields are text entry fields in add or edit mode.
Use the Edit option when you need to change an existing mapping.
Click Update to save any changes.
SSH Tunnel
The SSH Tunnel tab provides the means to add SSH tunneling information to establish a secure tunnel to the collection system.
You will need to add the SSH Server address and the required credential, which you can either add via the + or select from a list of pre-configured Credentials.
Set the Enable SSH Tunnel checkbox to use the tunnel and click Update to save any changes.
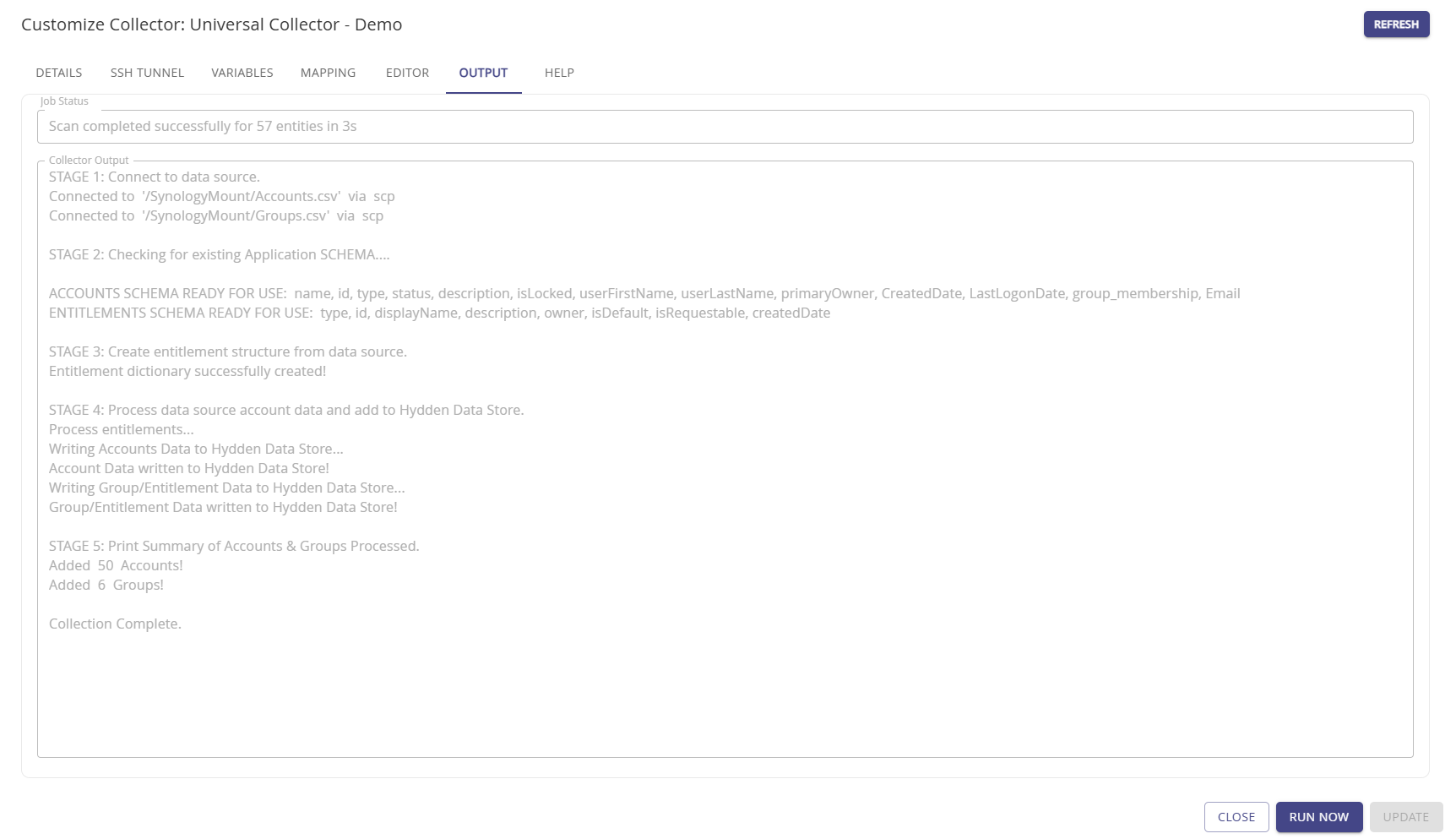
Output
The Output tab provides a collector status based on the last run. It's shows the Job Status information, and the Collector Output detailing the job processing stages and results.
Help
Use the Help tab for details on how to collect from different data source formats.
- Hydden Module: The module provides functions to create and store entities to the Hydden Identity Graph.
- CSV Module: The CSV module provides functionality for parsing CSV (Comma Separated Values) data within scripts. It allows reading CSV data from strings or bytes, specifying delimiters, handling headers, and iterating over rows.
- Expect Module: The module provides functions to read data from various URI schemes (file, scp, sftp, ftp, ftps) and return the content as a string.
- JSON Module: The module provides a JSON codec.
- LDAP Module: The module provides functions to read data from various URI schemes (file, scp, sftp, ftp, ftps) and return the content as a string.
- Math Module: A module of math-related functions and constants.
- REST Module: The REST module provides functions to read data from retrieve content from REST endpoints as a string.
- SQL Module: The SQL module provides a way to execute SQL queries from within scripts. It supports multiple database drivers, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MSSQL.
- Time Module: A module of time-related functions and constants.
- URI Module: A data collection module providing function to read data from various URI schemes (file, scp, sftp, ftp, ftps) and return the content as a string.
- XML Module: The module provides an XML parser.
